31. Next Permutation
Problem:
Analysis:
这题真无聊啊,这种类型的题面试如果之前没遇到过肯定挂。除非面试官提示规律,完全想不出来。
Solution:
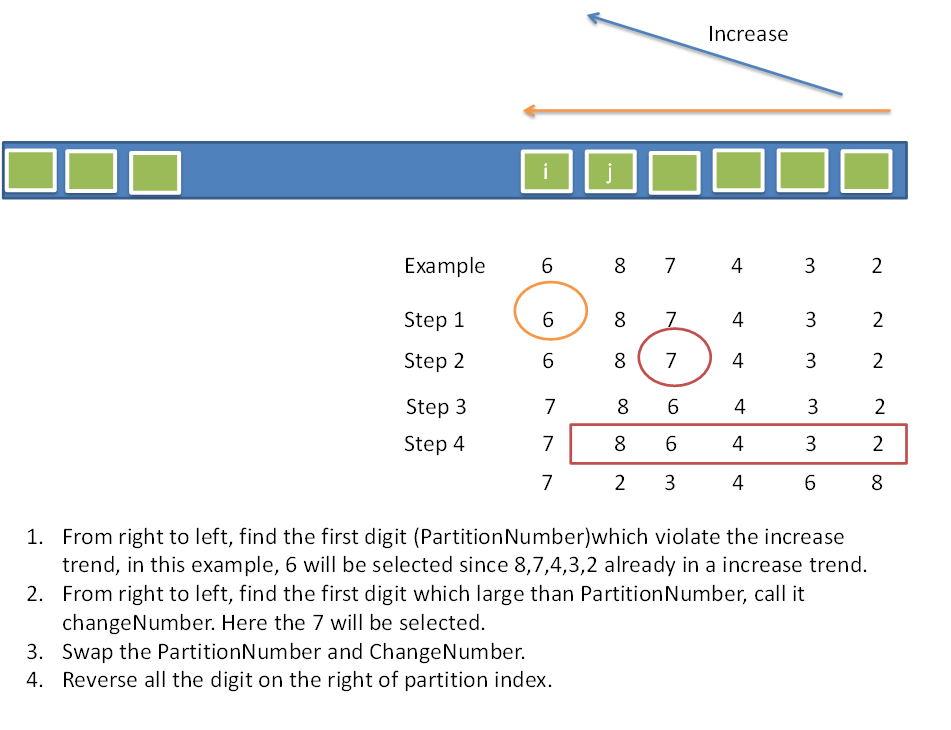
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (ie, sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in-place, do not allocate extra memory.
Here are some examples. Inputs are in the left-hand column and its corresponding outputs are in the right-hand column.
1,2,3 → 1,3,23,2,1 → 1,2,31,1,5 → 1,5,1Analysis:
这题真无聊啊,这种类型的题面试如果之前没遇到过肯定挂。除非面试官提示规律,完全想不出来。
class Solution { public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 || nums.length == 1) return; int p = -1; // partition index int c = -1; for (int i = nums.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) { if (nums[i] < nums[i + 1]) { p = i; break; } } // partition number not found reverse all. if (p == -1) { reverse(0, nums.length - 1, nums); return; } // find change index for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (nums[p] < nums[i]) { c = i; break; } } // swap swap(p, c, nums); // reverse from p to end reverse(p + 1, nums.length - 1, nums); } private void reverse(int start, int end, int[] nums) { while (start < end) { swap(start, end, nums); start++; end--; } } private void swap(int left, int right, int[] nums) { int temp = nums[left]; nums[left] = nums[right]; nums[right] = temp; } }
评论
发表评论