426. Convert Binary Search Tree to Sored Doubly Linked List
Problem:
Convert a BST to a sorted circular doubly-linked list in-place. Think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the previous and next pointers in a doubly-linked list.
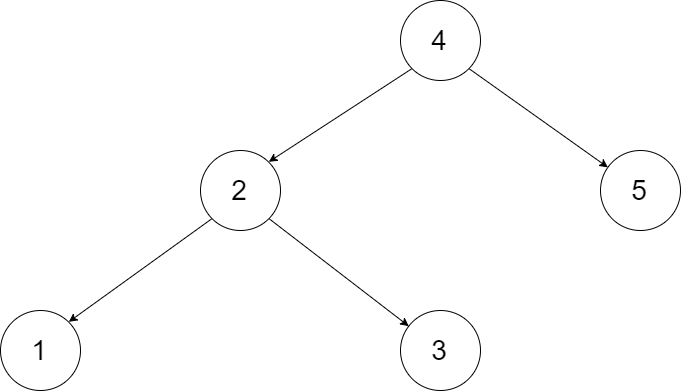
Let's take the following BST as an example, it may help you understand the problem better:

We want to transform this BST into a circular doubly linked list. Each node in a doubly linked list has a predecessor and successor. For a circular doubly linked list, the predecessor of the first element is the last element, and the successor of the last element is the first element.
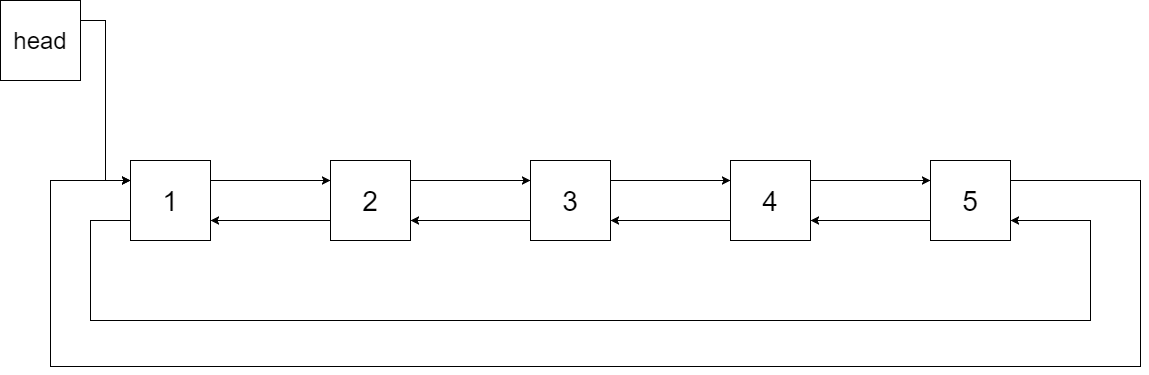
The figure below shows the circular doubly linked list for the BST above. The "head" symbol means the node it points to is the smallest element of the linked list.

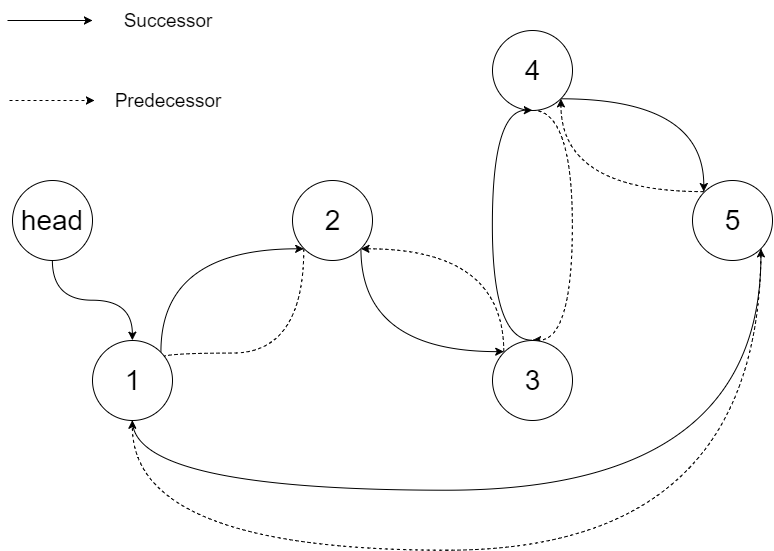
Specifically, we want to do the transformation in place. After the transformation, the left pointer of the tree node should point to its predecessor, and the right pointer should point to its successor. We should return the pointer to the first element of the linked list.
The figure below shows the transformed BST. The solid line indicates the successor relationship, while the dashed line means the predecessor relationship.

Analysis:
需要一个dummy,先把dummy指向prev,这样1就能和dummy连上了。inorder完成后,最后一个node就是prev,然后就可以把1和prev连上。
Solution:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | class Solution { Node prev = null; public Node treeToDoublyList(Node root) { if (root == null) return null; Node dummy = new Node(0, null, null); prev = dummy; helper(root); dummy.right.left = prev; prev.right = dummy.right; return dummy.right; } private void helper(Node root) { if (root == null) return; helper(root.left); root.left = prev; prev.right = root; prev = root; helper(root.right); } } |
评论
发表评论